What Are DAOs?
A Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) is an organization that is owned and managed by its own members, without the need for central governance.
A group of developers from the Ethereum community who were inspired by the principles of cryptocurrencies came up with the idea of a Decentralized Autonomous Organization in 2016. [1]Samuel Falkon – The Story of the DAO The idea was to create an organization that wasn’t governed by a central authority, so more power was given to investors and contributors to the organization.
A DAO is an internet-based business, governed by its set protocols. These protocols set the rules around spending within the DAO and are cemented within the code itself. The decisions within the DAO take place as a vote, this ensures that all members have an equal say in what decisions are made. [2]Ethereum – Decentralized Autonomous Organisations
How Do DAOs Work?
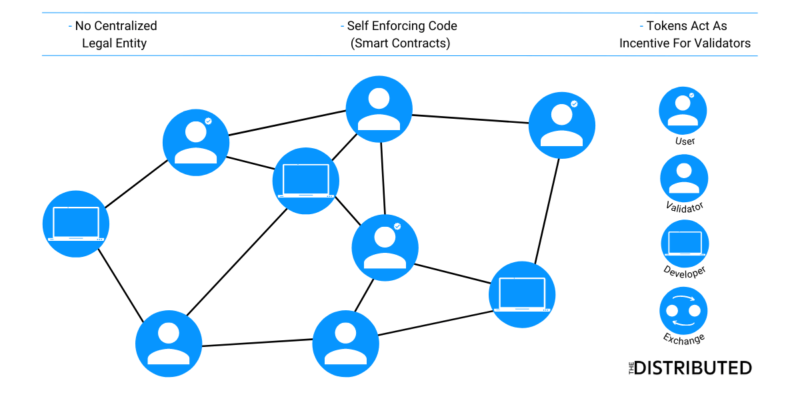
DAOs are peer-to-peer systems that operate through the use of smart contracts. These are programs stored within a blockchain that run when predetermined conditions are met. Smart contracts are immutable once deployed, so it is where the rules and protocols for the DAO are set in stone.
DAO governance is coordinated with the use of tokens or NFTs, these assets grant voting powers. Those who have a stake in the DAO, have voting rights and have the ability to potentially influence how the organization may operate through the creation of, or addition to governance proposals. A proposal will only pass through once a majority of (usually 51%) the DAO has agreed upon it. Although, the majority may change, depending on the DAO.
The transactions that take place in a DAO are encoded on a distributed ledger within a blockchain. This creates a fully autonomous and transparent system, allowing anyone in the DAO to view their own treasuries.
Why Do We Need DAOs?
As DAOs are an internet-based business model, it can be hard to build trust solely over the internet. Naturally, DAOs are coded in a way that allows the trust of the system to lie within the code and nothing else. The code is 100% transparent and open-source as they’re built upon smart contracts and blockchains.
| DAO | Traditional Organization |
|---|---|
| Democratized | Hierarchical |
| Voting required for changes | Voting can be done usually solely by the person/s running |
| Votes autonomously tallied by smart contract | Internal manual voting count and handling |
| Autonomous services; distribution of funds | Manual services, or controlled automation |
| Transparent and public | More secretive and private |
Examples Of DAOs
DAOs can function as various different business models. Some DAOs act as a charity, where funds are donated to the DAO and the voting decides where the funds are sent to, or some act as a venture fund, where investments in the DAO are pooled and spent on a larger investment that can then be split to the members of the DAO.
Here are some of the most popular DAOs since 2016;
| Name | Token | Use Cases | Network | Launch | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dash | DASH | Governance, Fund Allocation | Dash | MAY 2015 | Operational |
| The Dao | DAO | Venture Capital | Ethereum | APR 2016 | Defunct [3]https://www.gemini.com/cryptopedia/the-dao-hack-makerdao#section-origins-of-the-dao |
| MakerDAO | MKR | Governance, Fund Allocation | Ethereum | DEC 2017 | Operational |
| Steem | STEEM | Data distribution, Social media, Name services | Steem | MAR 2016 | Operational |
| Uniswap | UNI | Exchange, Automated Market Making | Ethereum | NOV 2018 | Operational |
| UkraineDAO | UD | Fundraising, NFT Sale | Ethereum | FEB 2022 | Defunct |
| ConstitutionDAO | PEOPLE | Purchasing an original copy of the United States Constitution | Ethereum | NOV 2021 | Defunct |
References



