What Do Blockchains Do?
Blockchain technology utilizes distributed ledger technology (DLT) to store and distribute information in a decentralized manner.
The information on a blockchain is stored in blocks, these blocks are chained together with other blocks to form an immutable database. This means that the data can be seen and verified by everyone, but it cannot be touched and changed by anyone.
It is within these blocks that the most recent transactions made on the blockchain are stored. On Bitcoins blockchain, blocks are added to the chain through the process of cryptocurrency mining. This is how information is added to the public ledger and also how new coins are added to the circulation, as miners are rewarded for their efforts.
What Is The Size Of Bitcoins Blockchain?
The average size of a bitcoin transaction was around 250 Bytes in 2014, [1]Bitcoin Talk – Gavin Andresen: A Scalability Roadmap whereas the average size of a Bitcoin transaction is around 580 Bytes in 2022. [2]TradeBlock – Bitcoin Historical Data
The current block size of Bitcoins blockchain is 1MB, although it used to be much bigger at 36MB. The average block is able to fit around 1900 transactions,[3]Blockchain.com – Average Transactions Per Block there are blocks that fit much more than this, but also blocks that fit much less. In 2022, the entire Bitcoin blockchain sits at over 402,000 MB[4]Blockchain.com – Blockchain Size, or around 374 GB.
After Bitcoin Segregated Witness (SegWit) was added to the blockchain in 2017, this gave blocks a theoretical size of 4MB. Over 80% of blocks use SegWit meaning there are several blocks larger than the 1MB limit. [5]Woobull Charts – Bitcoin Segwit Adoption
In contrast, there are also several blocks smaller than 1MB as Bitcoin clients are not obligated to fill a block up to 100%. By default, Bitcoin clients will fill their block up with ~50KB of high-priority transactions and ~700KB of highest-fee-per-KB transactions.[6]Bitcoin Release Notes, Gavin Andresen – Transaction Fees
Why Did Satoshi Decrease The Block Size?
Satoshi Nakamoto decreased the block size in 2010 when he was still the lead developer. Although it is not known exactly why he did this there are theories that it was to reduce the risk of spam and DoS attacks on the network.
It can also be theorized that because Bitcoins block time is 10 minutes, a smaller block size led to heightened decentralization, which is a key aspect of Bitcoin.
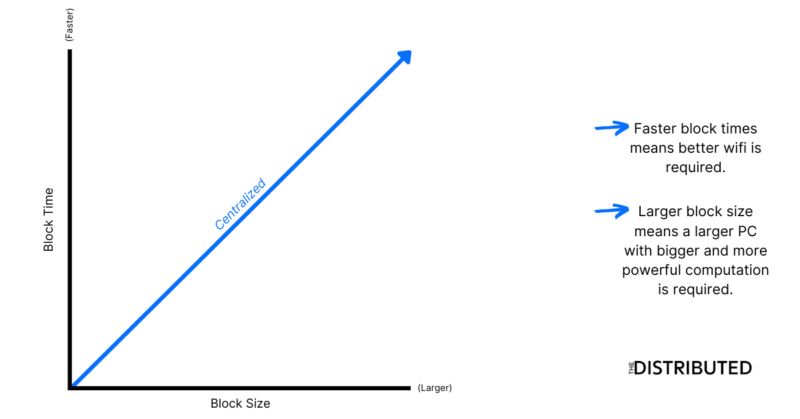
Average Bitcoin Block Size
The below chart shows the 30-day average size of a Bitcoin block, throughout the lifetime of Bitcoin.
With the traction Bitcoin has gained over the last few years there have been many newcomers to the industry. Those new to crypto may not want to go all in straight away, so they dollar-cost average with small Bitcoin purchases every week. But when they decide to transact this Bitcoin, they’re hit with high fees due to the input and output coins within their transaction.
Looking at the graph you can see once Bitcoin has become more accepted, the average block size increased dramatically.
References



