What Is A Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)?
A central bank digital currency (CBDC) is a virtual currency backed by a country’s fiat currency and issued by its central bank.
CBDCs were inspired by the increased popularity of virtual currencies based on a blockchain, like Bitcoin, although a CBDC is not a cryptocurrency. CBDCs differ from cryptocurrencies, being issued by a state and having an official legal tender status. So most CBDCs wouldn’t need a distributed ledger like a blockchain, as they are a centralized currency. [1]Wikipedia – Central Bank Digital Currencies
Although people have held money in a digital form through bank accounts or payment apps for a long time. A CBDC differs from existing digital money available to the general public as CBDCs monetary policy would be a liability of the Federal Reserve and not of commercial banks. [2]Federal Reserve – What Is A Central Bank Digital Currency?
Much like fiat, a CBDC is a form of money that would be included into existing financial systems and used for various purposes such as; digital payments, cross-border payments, domestic payments, and bank deposits.
Are CBDCs Stablecoins?
A central bank digital currency and stablecoin are used for the same purpose, to mimic physical currency in a virtual form. Despite this, stablecoins aim to be decentralized, and CBDCs aim at being a part of a centralized monetary system.
CBDCs work to expand financial inclusion in a nation, not reduce or replace them. [3]Federal Reserve – CBDC FAQs In contrast, cryptocurrencies like stablecoins work to replace and reduce the use of fiat currency.
Are CBDCs Cryptocurrencies?
A CBDC would be implemented with the use of a digital ledger controlled by the system implementing the currency, usually a central bank, government, or private entity. The database would use cryptographic protection and the appropriate security needed to protect its data being; the amount of money held by a certain entity.
Compared to cryptocurrencies, CBDCs would be centralized even using a distributed ledger, as a central entity is liable for it. Despite blockchain technology being the inspiration for such currencies, the use of the technology wouldn’t be needed for such a system. [4]Federal Reserve Bank of Boston – Project Hamilton Phase 1 Executive Summary
CBDCs vs Cryptocurrencies
| CBDCs | Cryptocurrencies | |
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain Type | Permissioned Blockchains (Private) | Permissionless Blockchains (Public) |
| Structure | Centralized | Decentralized |
| Anonymity | Linked to existing bank accounts and identity | Anonymous |
| Usage | Anything using fiat payments | Certain payments and speculation |
Types Of CBDCs
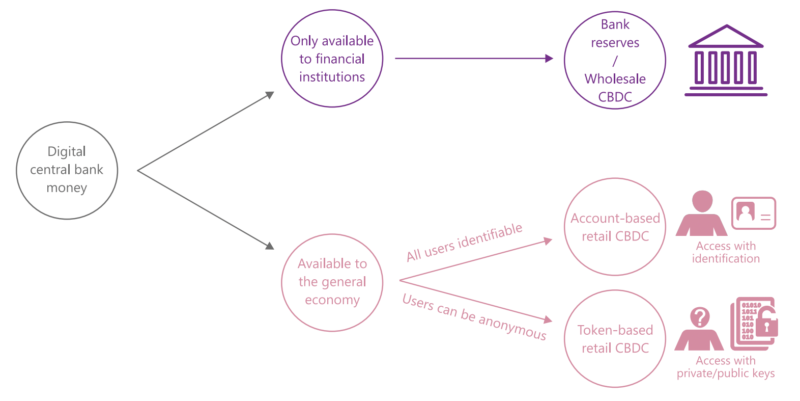
There exist two types of CBDCs, wholesale and retail. Wholesale CBDCs are primarily used by financial institutions, whereas retail CBDCs are used by consumers and businesses, similar to fiat currency. [5]BIS – Annual Economic Report
What Are Wholesale CBDCs?
Wholesale CBDCs will be used by financial institutions holding reserve deposits with a central bank. It could be used to improve payments and securities settlement efficiency while simultaneously reducing counterparty credit/liquidity risks.
What Are Retail CBDCs?
Retail or general-purpose CBDCs provide a safe, central bank instrument should the use of cash decline. These types of currencies would be used predominantly by both consumers and businesses.
How Many CBDCs Are There?
As of February 2023, there are 11 countries with an official CBDC. To add, there are 98 countries with CBDCs being researched, developed, or piloted. [6]Atlantic Council – CBDC Tracker The 11 countries with an official CBDC are;[7]Telangana Today – Here’s a list of countries to officially launch digital currencies
- The Bahamas
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Anguilla
- St. Kitts and Nevis
- Monserrat
- Dominica
- Saint Lucia
- Jamaica
- St. Vincent and the Grenadines
- Grenada
- Nigeria
References



