What Are Digital Signatures?
Digital signatures verify the authenticity of a message, document, or transaction through cryptographic encryption. A valid digital signature gives the receiver a strong conviction that the message is authentic and wasn’t altered along its path, as it is bound to a person or entity. This binding can also be further verified using blockchain technology.
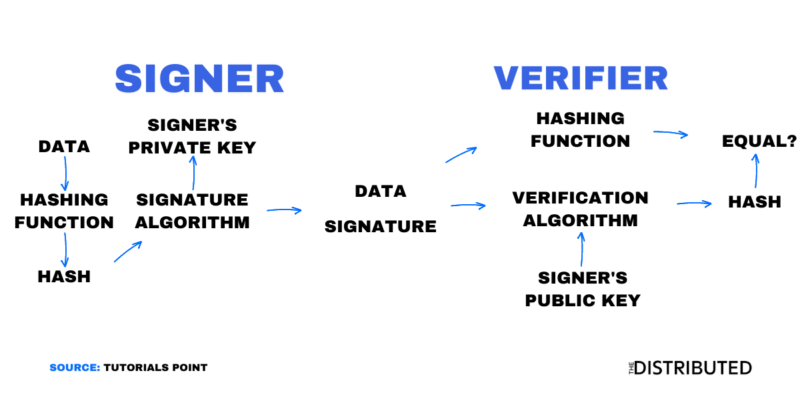
How Do Digital Signatures Work?
Digital signatures work through public-key cryptography, namely public and private keys. The public key represents your public details and the private key represents your private details.
Users are able to send messages to each other, verifying the legitimacy of the message using their private key. This is done by using your private key in a signing algorithm, which users can use your public key to verify that it came from your private key.
Messages being sent between users are hashed which ensures that it cannot be read and the pre/post hash can be compared to see if there were any changes in the message.
Applications For Digital Signatures
Message Authentication is the key application for digital signatures as it allows the reciever to verify if a message was received from who it was sent by.
Data Integrity means that if a message was intercepted by bad players, then the hash being verified won’t equate to the hash from the signer, this quickly deduces the legitimacy of the message.
Non-repudiation is the inability to refute responsibility. Verifiable digital signatures mean that one cannot deny the signing of a certain document – making for stronger legal cases and problem-solving.
References



