What Are Stablecoins?
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies with a value pegged to a reserve asset, which can help stabilize the price of the cryptocurrency.
Stablecoins are generally created, or “minted,” in exchange for fiat currency that an issuer receives from a user or third party.[1]US Treasury – Report on Stablecoins So for every stablecoin there should be an equal counterpart of the underlying asset in reserve as collateral, which can be cashed out upon request.
What Do Stablecoins Do?
Stablecoins were created to bring the pros of fiat and cryptocurrency together. They utilize the privacy, security, and processing time of cryptocurrencies and the stable valuations of fiat currency.
Stablecoins solve the problem of volatility linked with cryptocurrencies. This makes the adoption of crypto hard for a majority of people who cannot risk extreme volatility as they expect to know how much money they have in their bank, to manage their finances. With an asset pegged to a more stable currency holders can be more certain that their tokens won’t suddenly rise or crash.
Many of the stablecoins currently in circulation are underpinned by public blockchain networks, which provide security and transparency through the use of distributed ledger technology (DLT), this is one reason they’re preferred over traditional fiat.
Currently, stablecoins are used predominantly to facilitate trading, lending, and borrowing of digital assets.[2]US Treasury – Report on Stablecoins They make the process of purchasing digital assets on the blockchain seamless, reducing the need for fiat currency and intermediaries like financial institutions.
Why Are Stablecoins, Stable?
Asset-back cryptocurrencies like stablecoins have a huge advantage over traditional cryptocurrencies. As the underlying asset isn’t correlated with the market itself, it isn’t affected by its inherent volatility of it. Although it is important to note that stablecoins are subject to the same volatility and risk associated with their underlying asset.
The following graph compares the volatility of Bitcoin against the US Dollar, compared to the volatility of the Euro against the US Dollar.
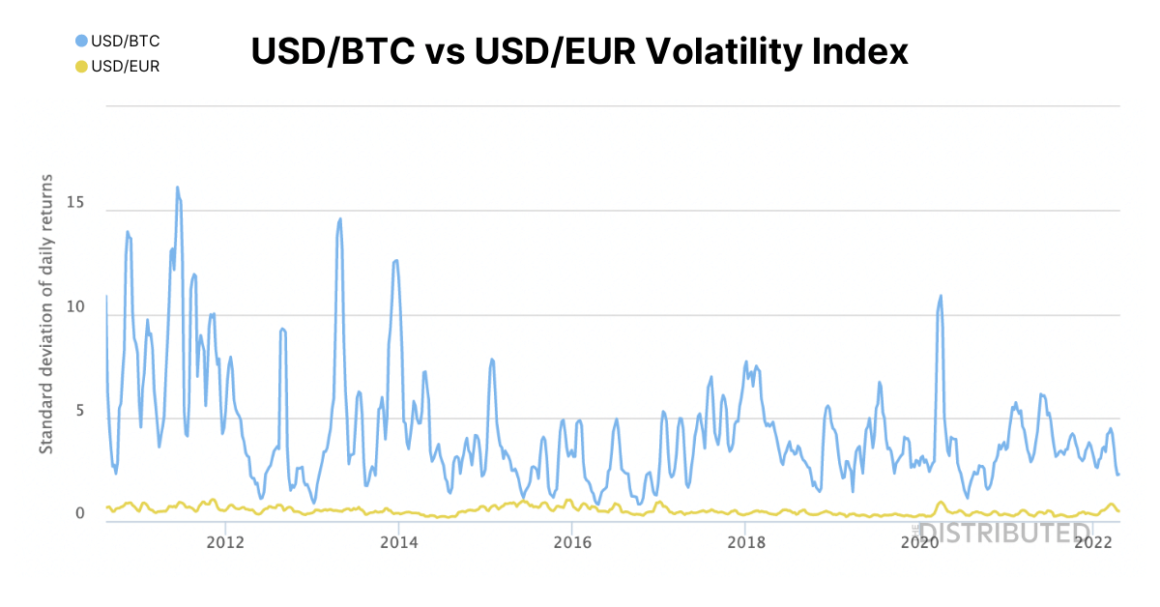
Source: buybitcoinworldwide.com / highcharts.com
Types Of Stablecoin Collateral
- Fiat Collateralized: The most common reserve asset used as collateral is fiat currency, typically USD. These cryptocurrencies are pegged 1:1 with the underlying currency.
- Precious Metals: There are cryptocurrencies that are backed by precious metals. The two most common precious metals used are gold and silver.
- Non-Collateralized: Digital assets that aren’t collateralized are typically algorithmic, meaning a stable price is retained by a working algorithm that will increase/decrease token supply as needed.
- Crypto Collateralized: Some cryptocurrencies will use other cryptocurrencies as their collateral.
- Mixed-Collateral: There are stablecoins that use various asset classes to back their coin.
Pegged vs Collateralized Stablecoins
Pegged digital currencies are those that are linked to the specific value of a bank-issued currency or another commodity. Whereas collateralized currencies are almost entirely backed by collateral which is held in a reserve.
The Most Popular Stablecoins
| Name | Ticker | Reserve Asset | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tether | $TUSD | USD Pegged. Collateralized by mixed assets. | $1.00 |
| Tether Gold | $XAUT | Gold Pegged. | $1,938 |
| USD Coin | $USDC | USD Pegged. Collateralized by mixed assets. | $1.00 |
| Dai | $DAI | USD Soft-Pegged – Collateralized By Multiple Cryptocurrencies. | $1.00 |
| XSGD | $XSGD | Fully Collateralized, Singapore Dollar Pegged. | $0.73 |
| Rai Reflex Index | $RAI | Algorithmic, Non-collateralized, Ethereum backed. | $3.00 |
References



